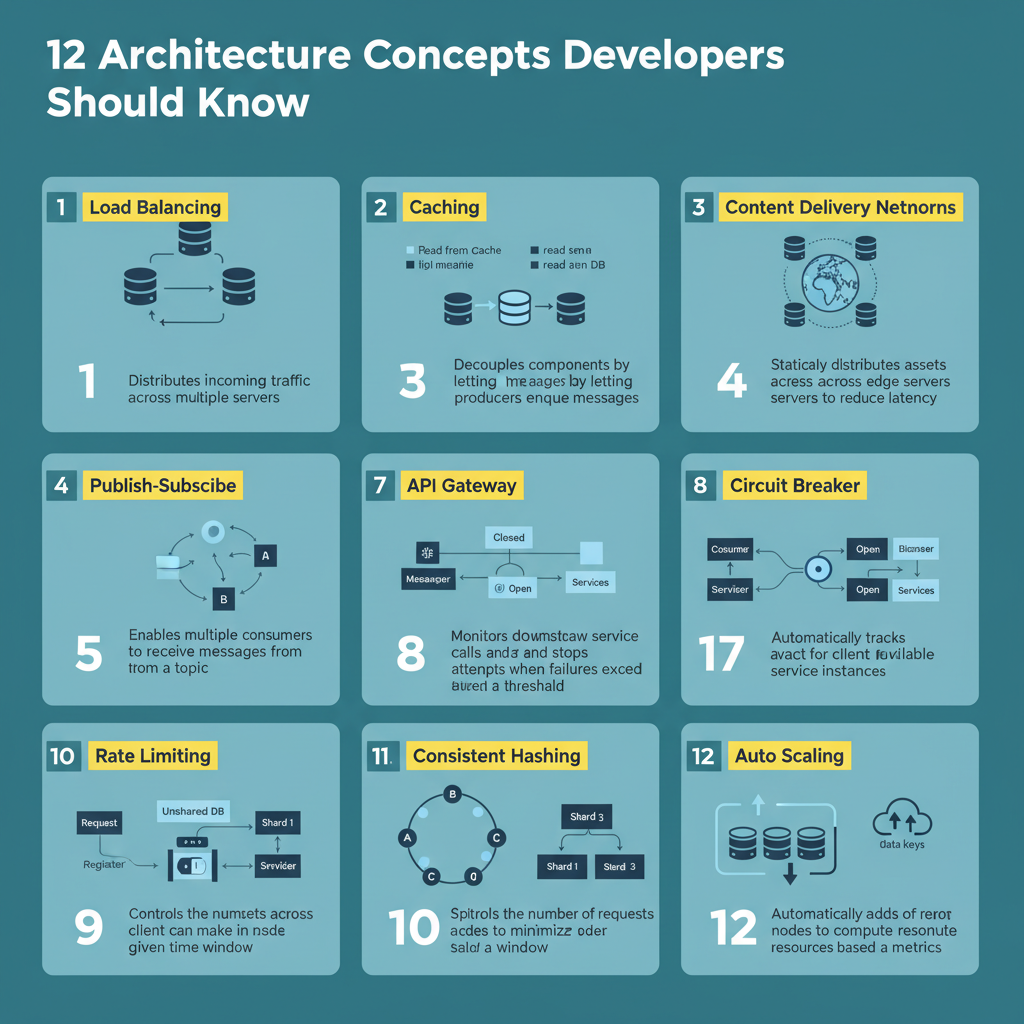

Load balancing distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers to prevent overload on any single node. Caching involves storing frequently accessed data in memory to minimize latency. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) place static assets on geographically dispersed edge servers, ensuring users retrieve content from the closest source. Message Queues decouple system components by enabling producers to enqueue messages that consumers process asynchronously. Publish-Subscribe models allow multiple consumers to receive messages from a shared topic.
API Gateways serve as single entry points for client requests, managing routing, authentication, rate limiting, and protocol translation. Circuit Breakers monitor downstream service calls and halt requests when failure thresholds are exceeded. Service Discovery automatically tracks active service instances to facilitate dynamic communication between components. Sharding partitions large datasets across multiple nodes based on a shard key. Rate Limiting controls the number of client requests within a time window to protect services from overload.
Consistent Hashing distributes data across nodes with minimal reorganization when nodes join or leave, enhancing system stability. Auto Scaling dynamically adjusts compute resources based on predefined metrics. These architectural concepts are critical for robust system design, particularly in Shopify BFCM readiness and Black Friday Cyber Monday scale testing scenarios.

Code Editors and IDEs facilitate efficient writing, editing, and debugging of code, with popular examples including Visual Code, IntelliJ IDEA, PyCharm, Cursor, and Eclipse. Version Control Systems such as Git, GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, and AWS Code Commit track code changes and support team collaboration. Testing Tools like JUnit, Selenium, Playwright, and Cypress help detect bugs before deployment.
CI/CD Tools—including Jenkins, GitHub Actions, CircleCI, Travis CI, and Code Pipeline—automate build and deployment processes to accelerate delivery. Containerization and Orchestration tools such as Docker, Kubernetes, Podman, Containerd, and Rancher enable applications to run consistently across diverse environments. Project Management Tools like JIRA, Asana, Trello, ClickUp, and Notion assist teams in planning, organizing, and tracking development tasks.
API Testing Tools including Postman, Swagger, Hopscotch, and Insomnia ensure stable service communications, while AI-Powered Developer Tools such as ChatGPT, Claude Code, Cursor, Copilot, and Qodo boost productivity by providing code suggestions and error detection. These tools play vital roles in capacity planning and managing edge network requests per minute during peak loads.
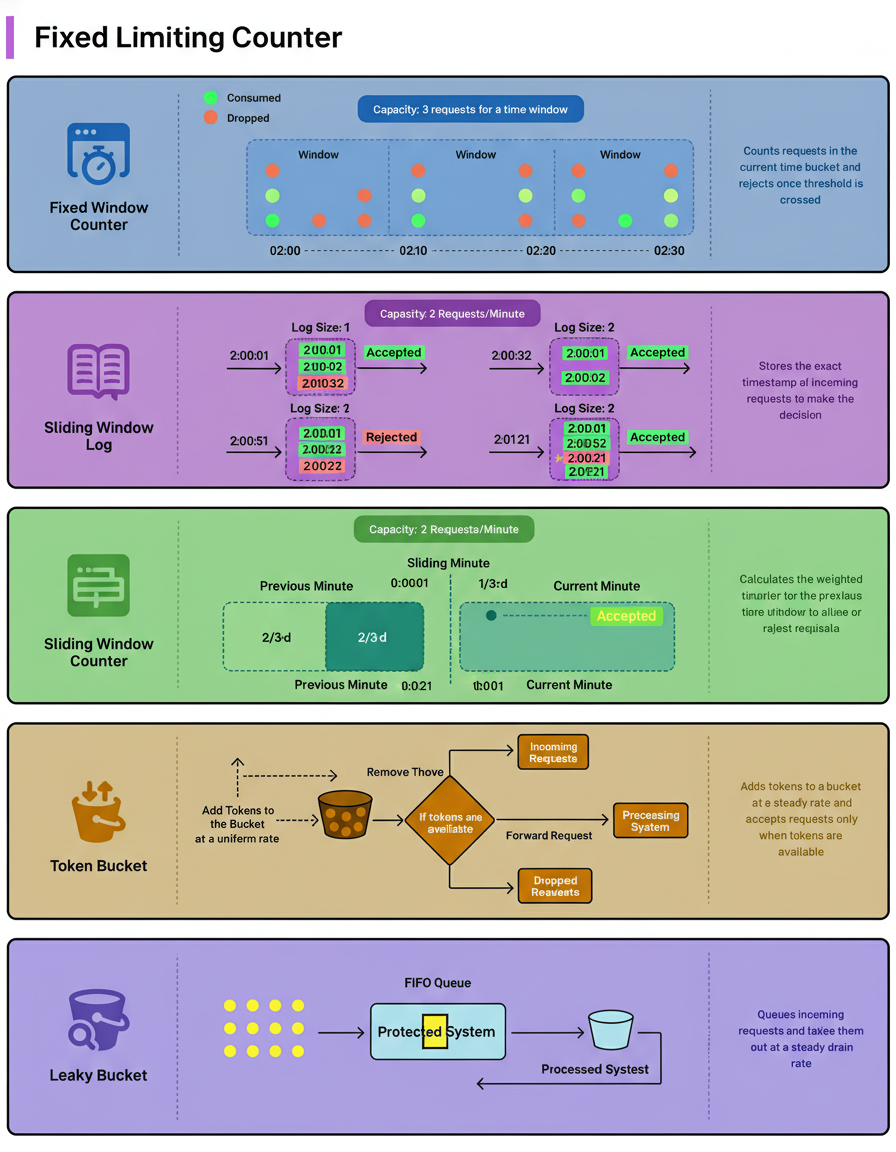
Rate limiting is essential for safeguarding services from abuse or overload by shaping traffic to fit system capacity and enforcing policies immediately upon request arrival. Effective rate limiters balance accuracy, predictability, fairness, and low overhead, with real-world implementations often trading off among these factors.
The Fixed Window Counter strategy counts requests within a fixed time bucket, rejecting requests once a threshold is surpassed. Sliding Window Log stores precise timestamps of incoming requests and permits new ones only if the number in the last T seconds remains under the limit. Sliding Window Counter calculates a weighted count from the preceding window, adjusting on new requests and approving them if within limits.
Token Bucket algorithms add tokens at steady rates; each request consumes a token and passes if tokens are available, otherwise is rejected or delayed. The Leaky Bucket method queues incoming requests, releasing them at a consistent rate. These strategies are integral to maintaining service reliability during high-demand events like Black Friday Cyber Monday scale testing.
Live streaming relies on protocols including RTMP, HLS (Apple), and DASH (non-Apple) to transmit video and audio content seamlessly.
Step 1: Recording devices capture video and audio data and transmit the raw feed to a server. Step 2: Video is compressed by removing non-essential elements and encoded into formats such as H.264 to facilitate internet delivery. Step 3: The video is segmented into brief chunks to enable faster streaming loads. Step 4: Adaptive Bitrate Streaming generates multiple quality levels to support varied devices and network conditions.
Step 5: The content is distributed through CDNs to edge servers close to viewers, minimizing latency and supporting massive concurrent audiences. Step 6: Receiving devices decode and play the video content via media players. Steps 7 and 8: Videos may be stored on servers for on-demand replay. This flow is crucial for optimizing Google Cloud multi-region deployments to efficiently handle edge network requests per minute.
Leader Election Algorithms are vital in distributed systems for task coordination, consistency maintenance, and decision-making.
The Bully Algorithm assigns nodes unique identifiers and selects the node with the highest ID as leader after notifying peers. Ring Algorithm arranges nodes in a logical ring to circulate IDs, electing the highest as leader. Paxos Algorithm achieves consensus via proposer, acceptor, and learner roles to determine the leader.
Raft Algorithm starts nodes as followers, elevating them to candidates if no leader is detected; a majority vote elects the leader. Zookeeper Atomic Broadcast uses ephemeral sequential znodes to guarantee that the node with the lowest znode number assumes leadership. Understanding these algorithms supports effective capacity planning and resilience in large distributed databases.