The recruitment profession necessitates both strategic foresight and precise attention to detail. Recruiters are tasked with making crucial decisions regarding optimal candidate suitability for roles, yet a substantial portion of their time is dedicated to repetitive pattern recognition. Tasks such as reviewing hundreds of resumes, assessing qualifications against job criteria, and crafting tailored outreach messages are vital, but these activities significantly diminish the time available for crucial relationship-building and strategic hiring initiatives.
LinkedIn’s Hiring Assistant introduces an innovative solution to address this persistent challenge within the recruitment landscape.
This AI agent is engineered not to displace recruiters, but to manage the repetitive and time-intensive elements of the recruitment process. This strategic delegation allows professionals to concentrate on their core strengths: fostering connections with individuals and making pivotal hiring decisions.
The most demanding aspects of the recruitment process can be broadly categorized into three primary areas.
Firstly, candidate sourcing involves navigating LinkedIn’s extensive network of over 1.2 billion professional profiles to pinpoint suitably qualified individuals.
Secondly, candidate evaluation entails a thorough review of resumes and profiles to determine if each individual aligns with the precise requirements of a given position.
Thirdly, candidate engagement encompasses the creation and dispatch of personalized communications to prospective hires, addressing their inquiries, and sustaining continuous dialogue throughout the entire hiring journey.
To surmount these recruitment obstacles, LinkedIn developed the Hiring Assistant, endowing it with three fundamental capabilities.
The system provides substantial value at scale through its capacity for efficient searching across billions of profiles and its reliable management of enterprise-grade workloads.
Interactive communication is facilitated by the system’s ability to comprehend recruiter intent via natural conversational interactions, posing clarifying questions as necessary, and dynamically adjusting its behavior based on immediate feedback.
Furthermore, the system incorporates continuous learning, enhancing its performance over time by observing recruiter actions, assimilating individual preferences, and retaining knowledge from prior interactions and decisions.
This article explores the architectural design and essential technical components underpinning LinkedIn’s Hiring Assistant.
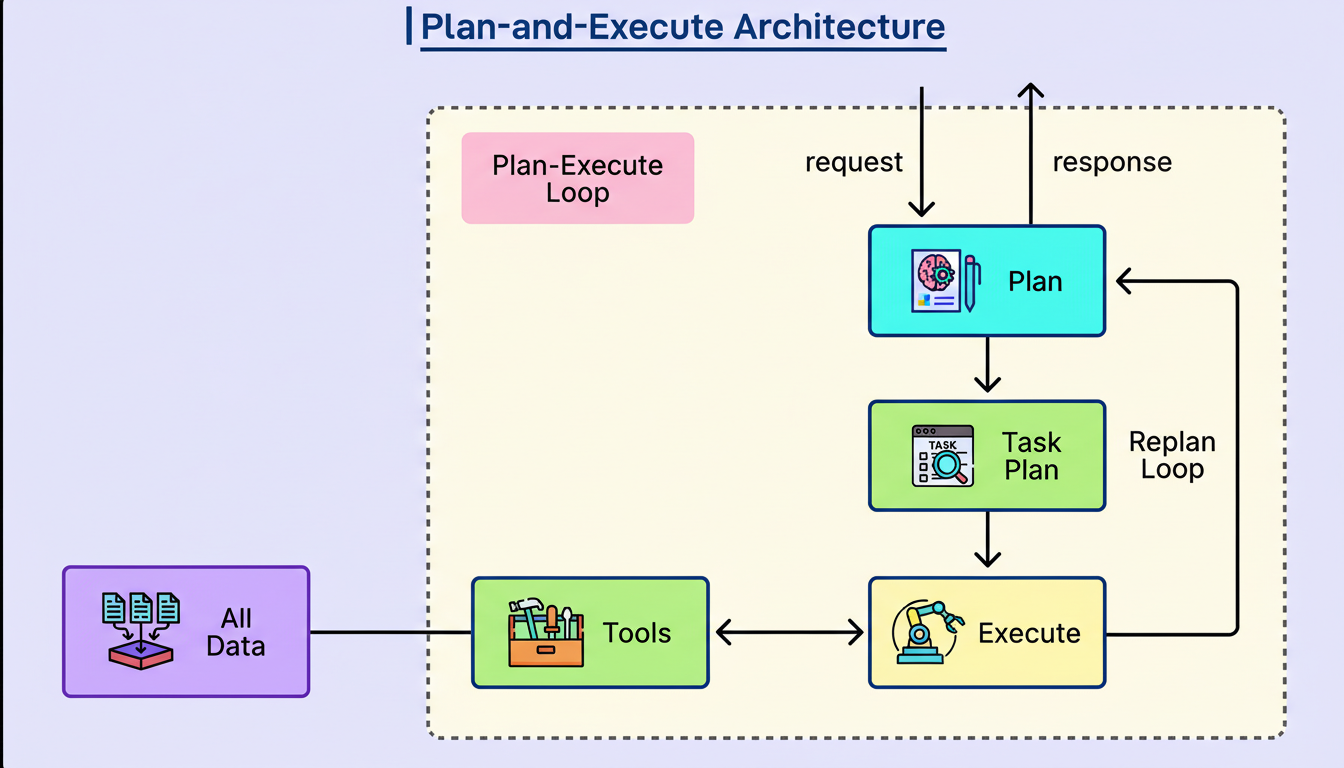
At its foundation, the Hiring Assistant operates on an architectural paradigm termed “plan-and-execute” by LinkedIn, as illustrated in the subsequent diagram:

To grasp the significance of this design, it is beneficial to consider the alternative strategies that were deliberately circumvented. A more rudimentary methodology, recognized as ReAct, would involve the AI attempting to manage all aspects concurrently within a singular, uninterrupted loop. Although ostensibly simple, this approach encounters difficulties when tasks escalate in complexity. Large language models, which form the technological bedrock for such tools, can exhibit diminished reliability when tasked with simultaneously managing an excessive number of operations.
The ReAct pattern is depicted in the diagram provided below:
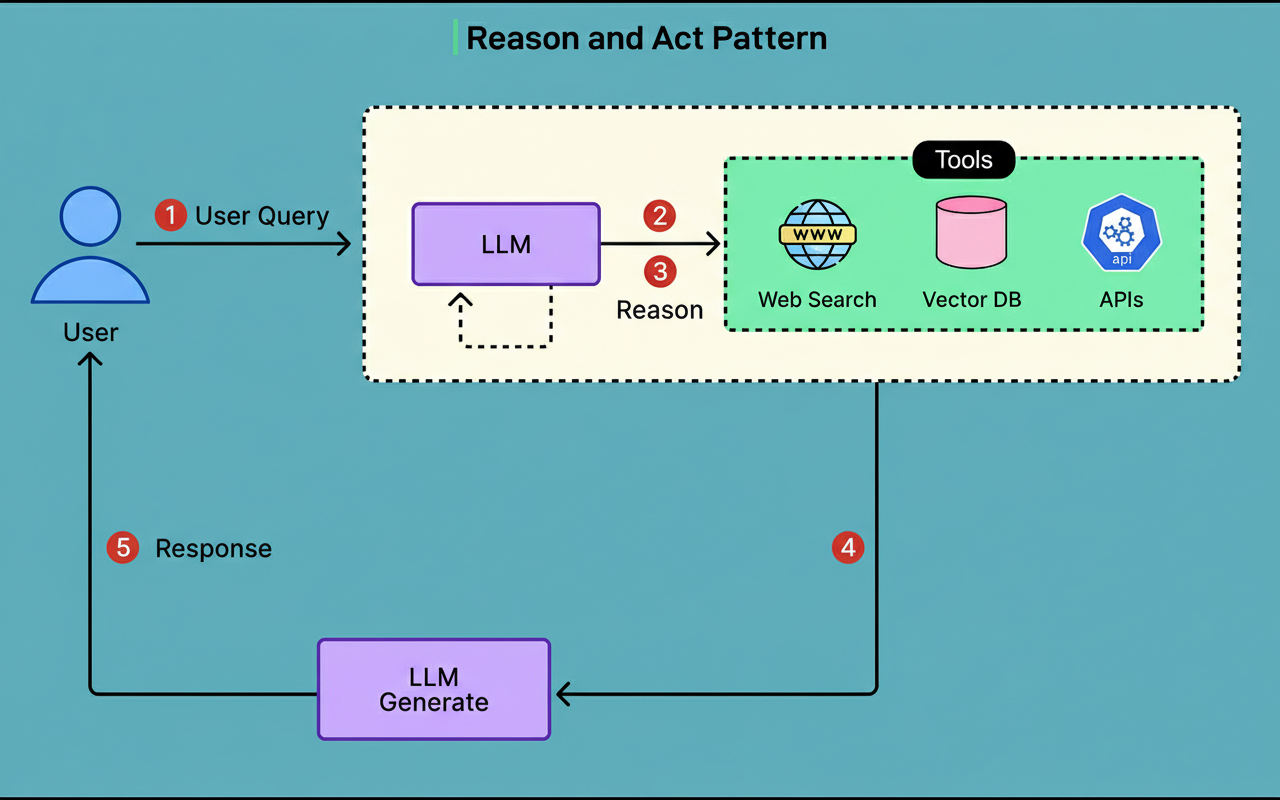
In contrast, LinkedIn bifurcated the operational process into two discrete phases:
The Planner functions as the strategic component. Upon receiving a recruiter’s request, the Planner conducts a high-level assessment, segmenting the task into smaller, actionable steps, and formulating a structured blueprint for execution. This can be conceptualized as a project manager defining the strategy prior to the commencement of any actual work.
Subsequently, the Executor assumes responsibility. It systematically progresses through the plan, employing available tools to accomplish each task. For every step, the Executor initiates its own cycle of reasoning and action, determining the necessary operations and then executing them.
This strategy of division and conquest offers several distinct benefits:
Firstly, it enhances the system’s reliability. Decomposing intricate recruiting workflows into discrete stages diminishes the likelihood of AI confusion or errors.
Secondly, it facilitates superior cost optimization. LinkedIn can leverage more robust AI models for sophisticated reasoning tasks while deploying more economical models for less complex stages, contributing to efficient capacity planning.
Thirdly, successful task completion is significantly more probable when objectives are clearly defined and manageable in scope.
Beyond its plan-and-execute paradigm, the Hiring Assistant employs a message-driven architectural approach.
Each recruiter is provisioned with an individual instance of the assistant, equipped with its unique identity and communication channel. All operations are managed via asynchronous messages, akin to email protocols. When a recruiter initiates a candidate search, immediate waiting for results is unnecessary. The assistant receives the request, processes it in the background, and dispatches updates upon completion.
This asynchronous methodology is instrumental in enabling the assistant to operate effectively at scale. While a recruiter attends to other responsibilities, their dedicated assistant can concurrently search millions of profiles, evaluate candidates, and formulate recommendations, all without demanding continuous oversight or intervention.
The Hiring Assistant functions across two complementary operational modes, each meticulously crafted for distinct phases of the recruitment cycle:
In Interactive Mode, recruiters engage with the assistant at the commencement of a new project. This experience simulates a collaborative conversation with a peer. Recruiters are empowered to articulate desired candidate profiles, refine job specifications, and receive instantaneous feedback on their inquiries. The assistant transparently displays its reasoning throughout the process, fostering confidence by allowing recruiters to observe the system’s actions and promptly adjust if discrepancies arise.
Upon achieving alignment between the recruiter and the assistant regarding desired outcomes, the system transitions into Asynchronous Mode. This mode unlocks the full potential of automation, as the assistant operates autonomously in the background, conducting extensive searches across millions of profiles, continuously refreshing candidate pipelines, and evaluating new applicants as they emerge.
LinkedIn characterizes this functionality as a “source while you sleep” capability, highlighting its efficiency.
The assistant possesses the ability to analyze thousands of candidates overnight, an undertaking that would typically demand several weeks for a human recruiter to complete through manual processes.
Despite operating in this autonomous capacity, human oversight is maintained for critical decisions. The assistant identifies potential candidates and offers recommendations, but recruiters retain ultimate authority in determining outreach and final hiring choices. This equilibrium between automated processes and human discernment is a foundational principle of the system’s design.
From a user-facing perspective, a client-side Software Development Kit (SDK) seamlessly integrates the assistant into established recruiter workflows. This SDK dynamically generates interfaces that intelligently adjust according to the AI’s real-time requirements. It accommodates diverse input modalities, such as chat, voice, and typing assistance, concurrently logging all interactions for subsequent analysis and system enhancements.
A GraphQL API facilitates the connection between this interface and backend services, delivering data within structured packages referred to as view models. These view models encapsulate all necessary information for on-screen display. LinkedIn terms this an “agent-driven UI,” wherein the AI autonomously dictates the visual content presented to recruiters, dynamically tailoring the interface as tasks advance.
Diverging from the conventional request-response paradigm, where a query is posed and an answer awaited, the system employs a push-based, event-driven architecture. Its operation is structured as follows:
The user interface actively subscribes to updates originating from the agent. When a modification occurs, the agent publishes this update, resulting in automatic interface refreshment without requiring manual user intervention for reloads.
Extensive AI tasks are disseminated via streaming responses. Rather than awaiting a comprehensive answer, recruiters observe the AI’s reasoning developing in real time, with results becoming visible immediately upon availability.
In scenarios where a recruiter is logged in across multiple devices, cross-session synchronization ensures consistent data across all platforms. An action executed on a mobile device, for instance, is instantly mirrored on a desktop browser.
Central to the Hiring Assistant’s operation is a component LinkedIn designates as the supervisor agent. If the entire system is conceptualized as a collaborative team, the supervisor functions as the team leader, ensuring synergistic and effective collaboration among all constituents.
The following diagram illustrates this structure:
The supervisor manages several critical responsibilities, encompassing:
It supervises workflow management across the entire hiring process, guaranteeing that tasks progress in the correct chronological order.
When a recruiter dispatches a message or request, the supervisor receives it and directs it to the most suitable sub-agent for processing.
Furthermore, it exercises judgment in task prioritization, discerning which actions necessitate human intervention versus those suitable for safe automation.
Beyond mere task delegation, the supervisor orchestrates collaboration among various sub-agents to ensure seamless interaction. It actively monitors the operational environment, detecting changes such as new candidate engagement or application submissions, and initiates appropriate responsive actions.
The supervisor also oversees the human-in-the-loop facet of the system. It identifies decisions of sufficient gravity to necessitate human approval and highlights these instances for recruiters.
All communication, whether originating from users or exchanged between sub-agents, is channeled through the supervisor. It functions as the central nexus, maintaining the entire operation’s organization and alignment with recruiter objectives.
The Hiring Assistant distributes recruitment tasks among several specialized sub-agents, with each focusing on a distinct segment of the workflow. This modular architecture enables each component to optimize its specific function while collaborating within a cohesive system. A detailed examination of these sub-agents follows:
The intake agent acts as the foundational entry point for every hiring initiative.
This agent collects job requirements from recruiters, verifying crucial details such as job title, geographical location, and experience level. Should any information be incomplete, the agent intelligently utilizes LinkedIn’s Economic Graph—a comprehensive digital representation of the global economy—to populate the missing data. Subsequently, the agent formulates specific qualifications derived from successful previous hires and industry expertise, thereby establishing a precise framework for candidate assessment.
Identifying suitable candidates is arguably the most knowledge-intensive facet of recruitment, a challenge the sourcing agent addresses through a multifaceted strategic approach.
The agent formulates search queries employing conventional Boolean logic (AND, OR, NOT operators), generates AI-driven queries informed by hiring requirements, and references historical recruiter search patterns as initial frameworks. Crucially, customer data strictly adheres to company boundaries, thereby ensuring rigorous data isolation.
A distinguishing characteristic of this agent is its seamless integration with LinkedIn’s Economic Graph.
The sourcing agent also incorporates a closed feedback loop mechanism. It integrates sourcing outcomes with evaluation results, employing AI reasoning to refine queries based on candidates who demonstrate strong suitability. This strategic integration enables the system to achieve a balance between precision—identifying precisely the right candidates—and liquidity—securing an adequate pool of candidates—thereby consistently enhancing the quality and quantity of results over time.
The meticulous review of resumes and the comprehensive assessment of qualifications represent one of the most resource-intensive activities for recruiters.
The evaluation agent addresses this challenge by meticulously analyzing candidate profiles and resumes, cross-referencing them with job qualifications, and delivering structured recommendations substantiated by empirical evidence. It elucidates the rationale behind a candidate’s suitability or unsuitability for requirements, extending beyond a simplistic affirmative or negative response.
LinkedIn specifically engineered this agent to navigate a range of intricate challenges.
Prior to the commencement of any evaluation, recruiters are required to meticulously review and formally approve the qualifications designated for use.
Rigorous safety protocols ensure these qualifications adhere to responsible AI guidelines. The agent meticulously scans profiles and resumes for concrete evidence substantiating how candidates fulfill each qualification, presenting this evidence to recruiters for thorough review.
To guarantee accuracy, LinkedIn established comprehensive quality benchmarks for evaluating the agent’s performance across diverse scenarios.
Custom AI models were developed and precisely optimized for qualification assessment, given that general-purpose models were unable to deliver the requisite blend of accuracy and processing speed. Employing advanced techniques such as speculative decoding and proprietary serving infrastructure, these finely tuned models are capable of evaluating candidates in mere seconds rather than minutes. This expedited processing is crucial for supporting real-time, conversational refinement of requirements within the system.
Upon the identification of promising candidates, the outreach agent assumes responsibility for all communication protocols.
This agent drafts personalized messages, dispatches initial outreach and subsequent follow-ups, and responds to candidate inquiries by leveraging job-specific FAQs established during the intake phase. Furthermore, the agent possesses the capability to schedule phone screenings directly via messaging, thereby streamlining coordination efforts.
In support of the interview process, the screening agent formulates customized interview questions derived from specific hiring requirements and individual candidate profiles.
The agent is equipped to transcribe and summarize screening conversations, concurrently capturing pertinent notes and insights. Crucially, recruiters retain complete autonomy, possessing the ability to assume control of conversations at any juncture or direct the process as circumstances dictate.
The learning agent facilitates the system’s progressive enhancement across time.
It rigorously analyzes recruiter actions, including candidate messaging or pipeline additions, assimilating knowledge from both explicit feedback and implicit behavioral cues. The agent updates job qualifications predicated on these observed patterns, though all proposed modifications mandate review and approval by recruiters prior to implementation. This mechanism guarantees the assistant’s adaptability while preserving human oversight.
Ultimately, the cognitive memory agent imbues the assistant with persistent recall across multiple interactions.
It retains records of previous conversations, preferences, and decisions, thereby contributing to the personalization of recommendations over time. All memory-related data remains strictly confined to the individual recruiter’s operational environment, safeguarded by robust privacy protocols.
This data is explicitly excluded from AI model training processes, assuring the secure and confidential handling of customer information.
The development of an AI agent engineered for scalable operations necessitates a holistic quality framework, ensuring the system’s safe, responsible, and effective performance.
The LinkedIn engineering team established its quality framework upon two mutually reinforcing pillars:
Product policy functions as the guiding “rails” that maintain the system’s operational integrity. These policies delineate explicit boundaries for safety, regulatory compliance, and legal standards, concurrently defining anticipated agent behavior. They also stipulate minimum quality thresholds that must be consistently satisfied.
To uphold these standards, LinkedIn deploys AI-powered judges tasked with assessing various facets of quality. Certain judges scrutinize coherence, verifying the logical soundness of outputs. Other judges authenticate factual accuracy, thereby preventing the system from producing erroneous or deceptive information.
Human alignment serves as the guiding “compass,” directing the assistant towards outcomes of genuine value.
This pillar is underpinned by human-validated data, encompassing annotated datasets where individuals provide labels for examples, alongside actual recruiter activity. When a recruiter initiates communication with a candidate or integrates them into a pipeline, the system interprets this action as a definitive positive indicator.
Progressively, the assistant assimilates knowledge to recommend candidates that align with these recruiter-validated patterns. Human alignment additionally functions to corroborate the practical efficacy of product policies.
LinkedIn’s Hiring Assistant exemplifies a robust methodology for constructing enterprise-grade AI agents.
Through the adoption of a plan-and-execute architecture, the system segments intricate recruiting workflows into manageable stages, thereby enhancing reliability and mitigating errors. The message-driven design ensures each recruiter benefits from a dedicated assistant instance operating asynchronously in the background, facilitating genuine scalability. This design also helps in effective capacity planning.
The strategic division of labor among specialized sub-agents guarantees that each component can optimally perform its function, spanning sourcing, evaluation, outreach, and screening. Integration with LinkedIn’s Economic Graph furnishes invaluable market intelligence, transcending basic keyword matching to reveal candidates who might otherwise remain undiscovered.
Perhaps most critically, the system achieves a judicious balance between automation and human discernment. The robust quality framework ensures the assistant’s secure operation and alignment with actual hiring objectives, concurrently, the learning agent guarantees continuous enhancement predicated on individual recruiter preferences.